Renewable Energy Climate Change

Popular Topics on Alternative Energy Sources Facts and Shifting weather Patterns
Five Principal Consequences of Climate Change
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges of our time, with far-reaching consequences for the planet and human societies.
Driven primarily by human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, climate change is altering Earth's natural systems in profound ways.
Below are five major effects of climate change that are already being observed worldwide.
1. Rising Global Temperatures
One of the most direct consequences of climate change is the increase in global average temperatures. According to NASA, Earth’s temperature has risen by about 1.2°C (2.2°F) since the late 19th century, with the past decade being the warmest on record.
Impacts:
- Heatwaves: More frequent and intense heatwaves pose health risks, especially to vulnerable populations.
- Shifts in Seasons: Warmer temperatures disrupt agricultural cycles and natural ecosystems.
- Permafrost Thaw: Melting permafrost releases stored greenhouse gases like methane, further accelerating warming.
2. Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets, Leading to Sea Level Rise
As global temperatures rise, glaciers, ice caps, and polar ice sheets are melting at unprecedented rates. Greenland and Antarctica alone are losing billions of tons of ice each year.
Impacts:
- Rising Sea Levels: Global sea levels have risen about 8–9 inches (20–23 cm) since 1880, threatening coastal cities and island nations.
- Increased Flooding: Higher sea levels lead to more frequent and severe coastal flooding and storm surges.
- Loss of Freshwater Sources: Many communities rely on glaciers for drinking water, which is now at risk.

3. More Frequent and Intense Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, droughts, wildfires, and heavy rainfall.
Impacts:
- Stronger Hurricanes: Warmer ocean waters fuel more powerful storms with higher wind speeds and rainfall.
- Prolonged Droughts: Regions like the southwestern U.S. and the Mediterranean face worsening water shortages.
- Increased Wildfires: Hotter, drier conditions lead to larger and more destructive wildfires (e.g., Australia 2019–2020, California wildfires).
4. Ocean Acidification
The oceans absorb about 30% of human-produced carbon dioxide (CO₂), leading to chemical changes that make seawater more acidic.
Impacts:
- Coral Bleaching: Acidification and warming waters stress coral reefs, causing mass die-offs.
- Marine Life Disruption: Shell-forming organisms (e.g., oysters, plankton) struggle to build their skeletons in more acidic waters.
- Fisheries Collapse: Declining marine biodiversity threatens global food security and fishing industries.
5. Disruptions to Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Climate change is altering habitats faster than many species can adapt, leading to shifts in migration patterns, breeding cycles, and food availability.
Impacts:
- Species Extinction: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that 20–30% of species face extinction if warming exceeds 1.5–2.5°C.
- Shifting Habitats: Animals like polar bears and penguins lose their natural environments due to ice melt.
- Ecosystem Collapse: Forests, wetlands, and marine systems face irreversible damage, affecting human livelihoods.
Conclusion
The effects of climate change are interconnected, amplifying risks to human health, food security, infrastructure, and global economies. Mitigation efforts, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy, and protecting natural ecosystems, are critical to limiting further damage. Adaptation strategies, including resilient infrastructure and sustainable agriculture, are also essential to cope with ongoing changes.
Addressing climate change requires urgent global cooperation to safeguard the planet for future generations.

Facts about Alternative Energy Sources and Changing Weather Trends

Understanding the implications and drivers of climate change in relation to sustainable energy is essential for comprehending the current global climate emergency. By examining the impact of renewable energy sources on the environment, we can gain valuable insights into their contribution to addressing this urgent issue. Renewable energy plays a significant role in mitigating climate change because it has the capacity to decrease greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.

An example of renewable energy is solar power, which captures the energy of the sun through photovoltaic panels. Solar power has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its environmental benefits and declining costs. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the capacity of solar power has been growing at a rate of over 20% annually since 2010. This expansion in the adoption of solar energy has resulted in a decrease in carbon dioxide emissions, aiding in the battle against climate change.
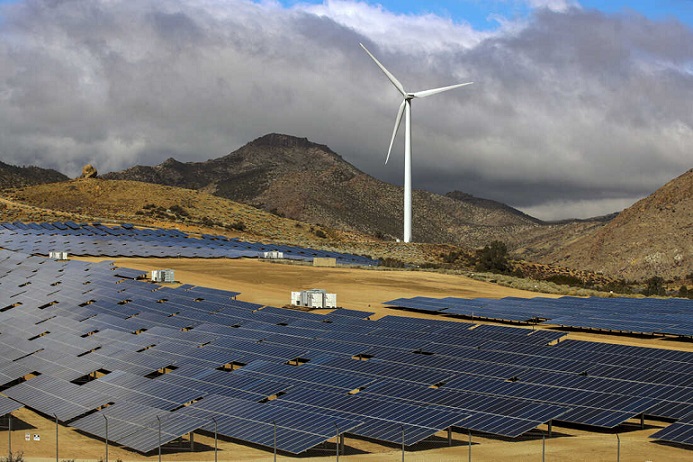

Another important source of renewable energy is wind power. Wind turbines convert the energy from wind into electricity, providing a clean and sustainable energy solution. The Global Wind Energy Council reports that the global installed capacity of wind power reached 651 GW by the end of 2020, highlighting its significant contribution to the renewable energy sector. By utilizing wind power instead of fossil fuels, we can reduce air pollution and mitigate the detrimental effects of climate change.

Renewable energy plays a crucial role in addressing the global climate emergency for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, which are the primary drivers of climate change. The combustion of fossil fuels like coal and oil releases substantial amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, resulting in heat trapping and the subsequent increase in Earth's temperature. By transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, we can significantly decrease these emissions and slow down the rate of global warming.

Additionally, renewable energy sources are abundant and widely accessible. Unlike fossil fuels, which have limited quantities and contribute to environmental degradation through extraction and combustion, renewable energy harnesses continuously replenished natural resources. This ensures a more sustainable and long-term solution to our energy needs while minimizing the adverse impact on the environment.

In conclusion, the connection between renewable energy and climate change is undeniable. Renewable energy sources offer a viable solution to the global climate emergency by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating the harmful effects of fossil fuel consumption, and providing a sustainable alternative. It is crucial to prioritize the adoption of renewable energy technologies to address this pressing issue and ensure a more sustainable future for future generations. For valuable insights and information on sustainable energy and its ecological implications, visit #FrizeMedia regularly and subscribe to our rss feed.
Nium, the Card Issuance Service, Partner With Tred to Supply Its Green Debit Card
UK-based green FinTech Tred has selected global B2B payments company – Nium – to be its card-issuance partner for its new sustainable product – the Tred green debit card. This will be the UK’s first green debit card that lets users track, reduce and offset their carbon footprint as they spend, and plants trees with profits.
Demand for green fintech solutions is booming and the financial sector is also embracing this trend, showing strong industry-wide support for ethical and sustainable financial services. Testimony to this demand is Tred’s waiting list, which has seen 122% growth since the start of 2021, and their recent crowdfunding round, which raised £1million from over 1000 investors. The card-issuance service provided by Nium will target UK residing customers and Tred will look to add reward programmes and benefits centred around the socially and ecologically conscious ethos as the programme progresses. “At our core, Nium’s mission is to enable businesses to meet their needs and goals through employing financial technology.
We are so happy and proud to join Tred on a mission to help people spend and live more sustainably through offsetting their carbon footprint with virtual financial services. This partnership will bolster Tred’s vision to be the platform that brings managing money and lowering our impact on the planet, effortlessly in one place”, says Frederick Crosby, Nium Chief Revenue Officer. Read more...
37% of heat fatalities due to climate – study
Wildlife under threat from climate Change - WWF
Prince Abdulaziz calls IEA's net-zero road map 'La La Land sequel'
Ocean Wave Power
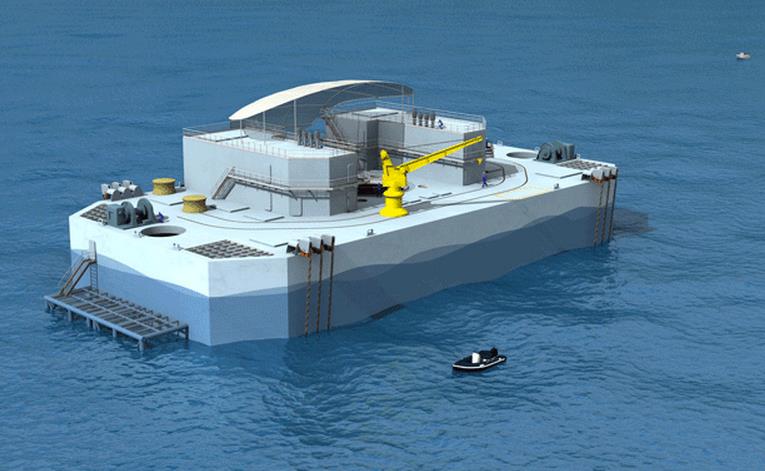
Alternative energy. Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) was conceived of by the French engineer Jacques D'Arsonval in 1881. OTEC is a potential alternative energy source that needs to be funded and explored much more than it presently is. The great hurdle to get over with OTEC implementation on a wide and practically useful level is cost. It is difficult to get the costs down to a reasonable level because of the processes presently utilized to drive OTEC. Ocean thermal energy would be very clean burning and not add pollutants into the air. However, as it presently would need to be set up with our current technologies, OTEC plants would have the capacity for disrupting and perhaps damaging the local environment. Read more...
COP26: Glasgow’s bid to plant 18 million trees in 10 years
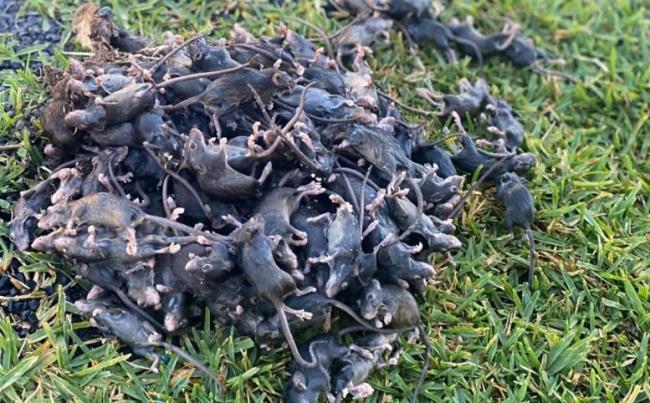
Claire Taylor: Mouse plague is a Shocking reminder of climate Dangers
DISTURBING accounts of a mouse plague gripping the east coast of Australia have served as a reminder of the growing severity of climate change and what could lie ahead for Scotland, if farmers aren’t properly equipped to tackle the impending challenges.
Heart-breaking reports from farmers living through the infestation and horrific footage to match, hardly begins to capture the extent of the damage millions of mice have inflicted on people’s crops, sheds, machinery and even their homes. Australian farmers have battled through years of bush fires and droughts, only now to have their crops destroyed by a mouse plague which isn’t looking like it is slowing any day soon. The recent dry conditions, coupled with a reduction in predator numbers due to the bush fires, has allowed breeding to explode. I spoke to one farmer who said the scale of the problem is “out of this world”. He spoke of farmers who had set traps, catching hundreds over night, but still weren’t even making a dent in numbers.
In desperation, the Australian government has applied for approval of a currently illegal poison known as bromadiolone to try and get to the bottom of the problem. A poison so powerful, New South Wales’ agriculture minister likened its potential use to “napalm for mice”. Read more...
Tweet
Follow @Charlesfrize










New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave a comment in the box below.